Ware·house: A large building where raw materials or manufactured goods are stored before their export or distribution for sale.
Manufacturing staffing is one of Bonney’s specialties. As a trusted warehouse and distribution staffing agency, it’s imperative that we keep associates safe on the job and can count on our client partners to keep their teams safe, too.
Since one of the ways to maintain a safety culture is through education, loosen your steel-toes, get comfortable (preferably in an ergonomic chair), and read on to learn how to avoid the most common warehouse safety hazards.
How a Warehouse Employment Agency Supports Workplace Safety
When partnering with a warehouse employment agency, clients not only gain access to skilled and qualified talent but also benefit from safety-first recruitment practices.
At Bonney Staffing, we prioritize placing candidates who are well-trained in safety protocols and understand the importance of workplace safety. This approach ensures that associates are equipped to handle the demands of a warehouse environment while minimizing risks.
Why Choose a Warehouse Employment Agency for Your Staffing Needs?
- Experienced Candidates: We connect businesses with employees who have experience in warehouse roles, such as forklift operation, stock handling, and general labor.
- Safety-Focused Screening: All candidates undergo rigorous screening to ensure they understand safety practices, including OSHA regulations and proper equipment handling.
OSHA’s 1910 Safety Standard
Whether your business manufactures, designs, or sells products, these settings include warehousing operations that support the business process. While the warehouse industry is not the most dangerous, there are hazards due to the type of work environment.
Some common warehouse occupations that are likely to be exposed to safety risks include (but are not limited to):
- General laborers and stock movers
- Stock clerks and picker and packers
- Powered industrial truck operators
- Shipping, Receiving, and traffic clerks
Warehouse operations fall under OSHA’s 1910 General Industry standard. Below, we’ve broken them down into ten common warehouse hazards. Plus, best practices to follow to maintain warehouse safety.
Warehouse Safety 101

1. Forklift Safety
Also known as OSHA 1910.178, industrial forklifts move materials/products. They serve as a means to reduce manual handling by workers. However, they also present hazards if improperly used.
What are the most common forklift safety hazards in a warehouse?
Forklifts are essential for moving heavy materials efficiently, but improper operation or lack of maintenance can lead to accidents, such as struck-by incidents, tip-overs, and collisions.
How can warehouse workers and employers ensure forklift safety?
- Ensure only certified operators use forklifts, with proper training to recognize hazards.
- Maintain forklifts regularly, checking brakes, tires, and hydraulics before use.
- Mark pedestrian pathways clearly, separating walking areas from forklift travel zones.
- Avoid exceeding the forklift’s load capacity, as this increases the risk of tipping over.
OSHA’s guidelines for powered industrial trucks recommend ongoing safety training and regular inspections to reduce risks.

2. Loading Dock Safety
Loading docks provide a means for loading and unloading large amounts of products into/out of storage for distribution. These areas can present struck-by and fall incidents.
Why are loading docks one of the most hazardous areas in a warehouse?
Loading docks involve heavy equipment and fast-paced activity, creating risks for falls, struck-by incidents, and collisions between equipment and workers.
What safety measures should be implemented for loading docks?
- Install barriers, guardrails, and warning signs at the edges of loading docks.
- Use wheel chocks to prevent trucks from accidentally rolling during loading or unloading.
- Keep dock areas clean and free of debris to prevent slips and trips.
- Train workers to follow specific procedures for safely entering and exiting dock areas.
OSHA emphasizes fall prevention and struck-by protection for dock safety. Partnering with a warehouse employment agency can also ensure workers are properly trained in dock safety practices.

3. Conveyor Safety
What are the main risks associated with conveyor systems?
Conveyors allow for quick and easy movement of product/goods/materials. However, they have the potential to cause caught-in and struck-by injuries.
How warehouses can improve conveyor safety:
- Clearly mark emergency stop buttons and educate workers on their location and use.
- Ensure all conveyors are equipped with proper guards to prevent access to moving parts.
- Regularly inspect belts, rollers, and pulleys to ensure they’re functioning safely.
- Restrict access to conveyor systems to trained employees only.
OSHA machine guarding standards illustrates proper maintenance and employee training regarding many types of moving pathways. These guidelines are critical components of warehouse safety when working with conveyors.

4. Hazardous Material Safety
Hazardous materials can pose a significant risk, if handled incorrectly. Improper storage and handling, insufficient training, and disposal of chemicals can result in serious injuries and property damage.
What are the biggest dangers of handling hazardous materials in warehouses?
Improper storage, labeling, and handling of hazardous materials can lead to chemical burns, fires, and exposure to toxic substances.
How can warehouses safely manage hazardous materials?
- Implement a Hazard Communication Program (HAZCOM) that complies with OSHA standards.
- Train all employees on how to read Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and recognize hazardous materials.
- Store chemicals in appropriate, labeled containers and provide proper ventilation in storage areas.
- Maintain spill kits and train employees on how to respond to chemical spills or leaks.
Bonney Staffing ensures workers placed in warehouses are familiar with HAZCOM protocols and can work safely with hazardous materials.

5. Manual Lifting Safety
Warehouses often have employees lifting products by hand, despite the adoption of assisted lifting devices (i.e., conveyors, pallet jacks, forklifts, etc.). Unfortunately, lifting activities can easily result in physical injuries (chronic or acute) to those workers who have to lift and move objects as part of their job.
Why is manual lifting a common cause of workplace injuries?
Improper lifting techniques and overexertion are major contributors to musculoskeletal injuries, such as sprains and hernias, in warehouse environments.
Best practices for safe manual lifting:
- Teach workers to lift with their legs, not their back, and avoid twisting while carrying loads.
- Use mechanical lifting aids like pallet jacks or forklifts whenever possible.
- Establish a two-person lift rule for items over a certain weight.
- Conduct regular ergonomic training to reduce strain and repetitive motion injuries.
According to OSHA, reducing manual lifting incidents can lower injury rates and improve overall warehouse productivity.

6. Ergonomics in the Warehouse
Ergonomics can help reduce and eliminate some of the more common injuries (i.e., musculoskeletal disorders, sprains, strains, etc.) caused by improper posture and repetitive movements.
How does ergonomics improve safety and efficiency in warehouses?
Ergonomics reduces the risk of repetitive strain injuries by designing tasks and workstations to match workers’ physical capabilities.
What ergonomic practices should warehouses adopt?
- Invest in adjustable workstations that accommodate workers of all sizes.
- Rotate workers between tasks to reduce repetitive motions and strain.
- Provide anti-fatigue mats for employees who stand for extended periods.
- Use ergonomic tools, such as adjustable pallet jacks, to reduce strain during lifting tasks.
Many warehouse employment agencies, like Bonney Staffing, prioritize matching workers to roles that suit their physical capabilities, ensuring safer and more efficient operations. OSHA has documentation on how warehouses can protect their manual laborers and reduce injuries.
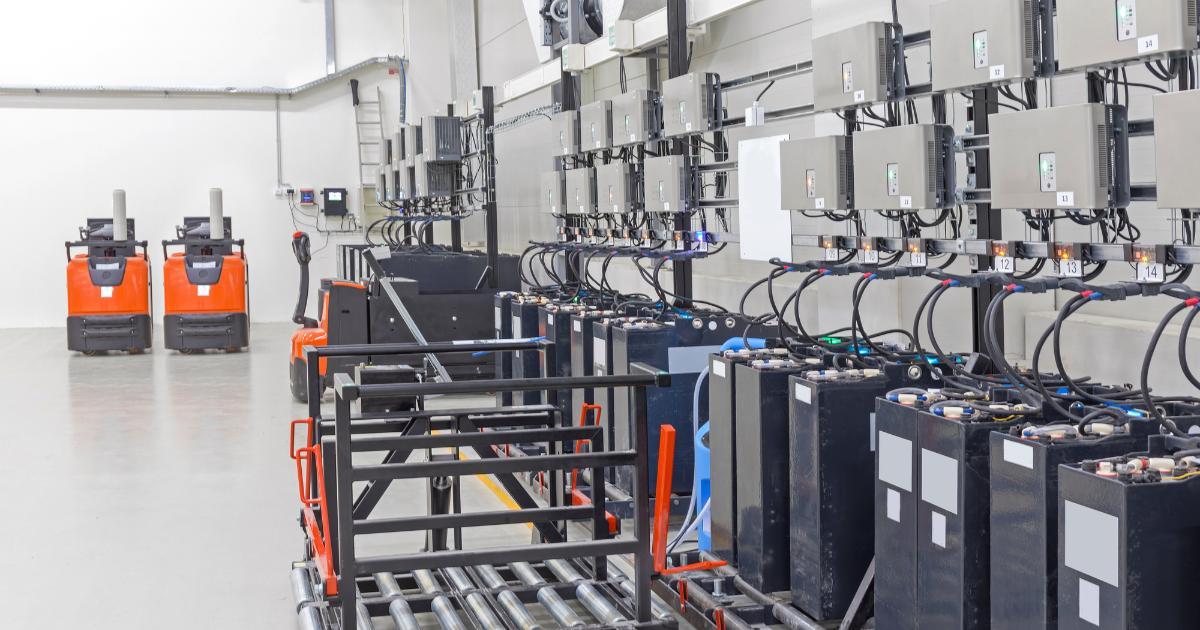

7. Charging Station Safety
Batteries and refuel powered equipment are the norm in modern warehouses. These stations can result in injuries if not maintained correctly, causing fires, burns, or chemical exposure.
Risks associated with warehouse charging stations:
- Improper handling of batteries and chemicals at charging stations can cause fires, burns, and chemical exposure.
- What precautions should workers take around charging stations?
- Maintain clear, organized charging areas, free from clutter and flammable materials.
- Regularly inspect equipment for signs of wear or damage, such as frayed cables.
- Ensure workers wear personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and goggles, when handling batteries.
- Train workers to recognize and respond to chemical spills or battery leaks immediately.
OSHA guidelines stress the importance of safe chemical handling and proper equipment maintenance to minimize risks in charging areas.

8. Material Storage Safety
Why proper material storage is critical in a warehouse
Improperly maintained, stacked, or loaded materials can lead to falling items that cause major injuries and property loss.
Best practices for material storage in warehouses:
- Keep heavier items on lower shelves and stack materials evenly to avoid tipping hazards.
- Use shelving systems with safety bars to prevent items from falling.
- Train workers on the safe handling of pallets and other storage equipment.
- Mark storage areas clearly, and enforce rules to keep walkways clear of obstructions.
A safety-first warehouse employment agency, like Bonney Staffing, ensures workers understand material storage guidelines before placement.

9. Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Energized equipment, or equipment that requires LOTO procedures can be extremely dangerous for the untrained. The most common mistake is employees bypassing safeguards while the equipment is running or servicing the equipment while energized.
What makes energized equipment so dangerous in warehouses?
Contact with energized equipment during maintenance or operation can cause electrocution, burns, or caught-in accidents.
How can warehouses implement safe LOTO procedures?
- Train all workers on the importance of de-energizing equipment before servicing it.
- Use lockout devices and tags to prevent accidental equipment startup.
- Conduct regular inspections to ensure LOTO procedures are followed.
- Prohibit unauthorized workers from bypassing safety mechanisms.
OSHA mandates LOTO training for all employees who work near or maintain energized equipment.
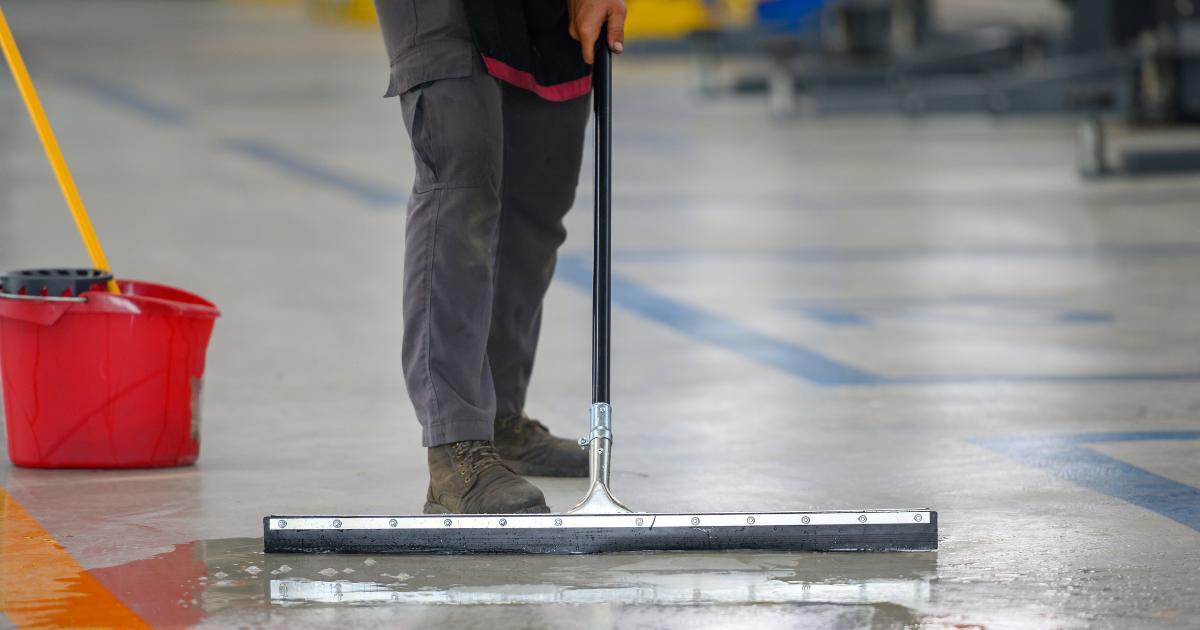

10. Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls
Why are slips, trips, and falls so common in warehouses?
Wet floors, cluttered walkways, and uneven surfaces contribute to a high number of preventable workplace injuries in warehouses.
Steps warehouses can take to reduce slips, trips, and falls:
- Install non-slip flooring and mats in high-risk areas.
- Encourage immediate clean-up of spills and debris.
- Provide proper lighting to ensure workers can see potential hazards.
- Conduct regular inspections to identify and address risks before they lead to incidents.
OSHA recommends keeping walkways clear and maintaining clean working surfaces as key steps to minimizing fall hazards.
Manufacturing Staffing and Safety
When it comes to warehouse and workplace safety, the tips above provide a solid foundation for recognizing common risks and addressing potential challenges.
By prioritizing hazard awareness training, conducting regular inspections, and implementing strong preventive measures, you can foster a safer environment for your team.
Partnering with a warehouse employment agency like Bonney Staffing adds an extra layer of support, helping you build a healthier, more productive workplace for everyone.